ProgressDialog
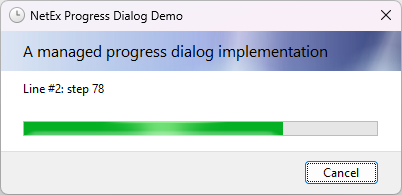
The ProgressDialog component is a pre-configured dialog box. It is the same Progress dialog box exposed by the Windows operating system. It inherits from the CommonDialog class.
The project aims to match standard .NET Framework and WinForms behaviour as closely as possible.
Use this component
If you have not already added it to your project, install the package from NuGet:
Install-Package NetEx.Dialogs.WinForms
Use this component within your Windows-based application as a simple solution for displaying progress in lieu of configuring your own dialog box. By relying on standard Windows dialog boxes, you create applications whose basic functionality is immediately familiar to users. Be aware, however, that when using the ProgressDialog component, you must write your own progress updating logic.
Use the ShowDialog method to display the dialog at run time in a modal fashion. Use the Show method to display the dialog at run time in a non-modal fashion.
When it is added to a form, the ProgressDialog component appears in the tray at the bottom of the Windows Forms Designer in Visual Studio.
Example
The following example uses the Windows Forms Button control's Click event handler to start a background task and then open the ProgressDialog with the ShowDialog method. The dialog will display the progress of the background task as it runs.
using NetEx.Dialogs.WinForms;
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class ProgressDialogForm : Form
{
[STAThread]
public static void Main()
{
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.Run(new ProgressDialogForm());
}
private Button selectButton;
private ProgressDialog progressDialog1;
public ProgressDialogForm()
{
progressDialog1 = new ProgressDialog
{
Maximum = 100
};
selectButton = new Button
{
Size = new Size(100, 20),
Location = new Point(15, 15),
Text = "Run task"
};
selectButton.Click += new EventHandler(SelectButton_Click);
ClientSize = new Size(330, 360);
Controls.Add(selectButton);
}
private void SelectButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Task.Run(() =>
{
progressDialog1.SetLine(1, "Doing background work...");
while (progressDialog1.Value < progressDialog1.Maximum)
{
progressDialog1.Value += 1;
progressDialog1.SetLine(2, $"Current value: {progressDialog1.Value}");
progressDialog1.Title = $"Worker task ({progressDialog1.Value}%)";
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}).ContinueWith(t =>
{
// Close the progress dialog after the task is complete
progressDialog1.Close();
}, TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext());
progressDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
}
Applies to
| Product | Versions |
|---|---|
| .NET Framework | 2.0, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 4.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6, 4.6.1, 4.6.2, 4.7, 4.7.1, 4.7.2, 4.8, 4.8.1 |
| Windows Desktop | 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 |